Earthquakes are natural disasters that have been affecting the world for millions of years. They are caused by the movement of tectonic plates, which make up the Earth's crust. Earthquakes can range from being barely noticeable to extremely powerful and destructive. In this article, we will delve into the details of earthquakes, including what causes them, how they are measured, and what can be done to prepare for and reduce the impact of earthquakes.
What Causes Earthquakes?
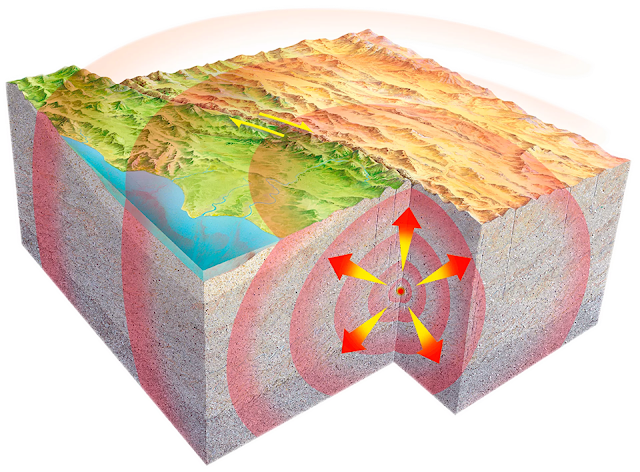
Earthquakes occur when two tectonic plates grind against each other, causing a release of energy in the form of seismic waves. This energy can cause the ground to shake, which is what we experience as an earthquake. Tectonic plates are huge sections of the Earth's crust that move slowly over time, often colliding with each other at their edges. When two plates collide, the edge of one plate can get stuck and build up pressure until it finally gives way, releasing the energy in the form of an earthquake.
In addition to plate tectonics, earthquakes can also be caused by human activities such as underground nuclear testing, the pumping of water into or out of the ground, and the extraction of oil or gas from the ground. These human-caused earthquakes, known as induced earthquakes, can be just as powerful as earthquakes caused by plate tectonics.
Measuring Earthquakes
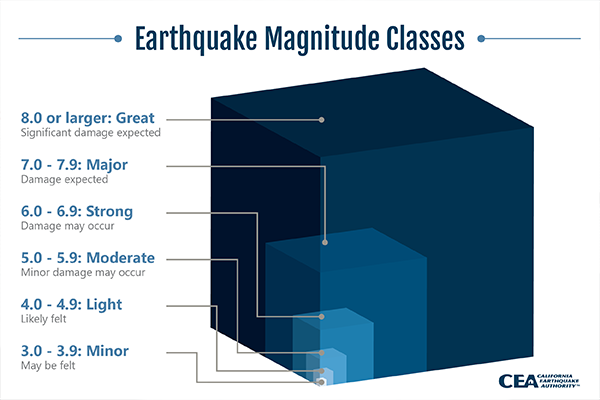
Earthquakes are measured using a scale called the Richter scale, which was developed by Charles Richter in 1935. The Richter scale measures the magnitude, or size, of an earthquake. The magnitude of an earthquake is determined by the amount of energy released by the earthquake, and is expressed as a number on the Richter scale. An earthquake with a magnitude of 2.0 or less is considered a minor earthquake, while an earthquake with a magnitude of 5.0 or higher is considered a moderate to strong earthquake. An earthquake with a magnitude of 8.0 or higher is considered a great earthquake, and can cause widespread damage and loss of life.
In addition to the Richter scale, earthquakes are also measured using the Moment Magnitude scale, which is a more accurate way of measuring the size of an earthquake. The Moment Magnitude scale takes into account not only the amount of energy released by an earthquake, but also the size and location of the fault that caused the earthquake.
Preparing for and Reducing the Impact of Earthquakes
There are several things that people can do to prepare for and reduce the impact of earthquakes. The first and most important thing is to be informed about the risks of earthquakes in your area, and to educate yourself about what to do in case of an earthquake. This can be done by obtaining information from your local government or by visiting websites dedicated to earthquake preparedness.
It is also important to have a disaster preparedness plan in place, which includes having an emergency supply kit on hand, knowing how to turn off gas and water valves, and having a designated meeting place for your family in case of an earthquake. Having a disaster preparedness plan can help reduce the stress and confusion that can occur during an earthquake, and can help ensure that you and your family are safe.
Another way to reduce the impact of earthquakes is to make sure that buildings are constructed to withstand earthquakes. This can be done by making sure that buildings are built to code, and by retrofitting older buildings to make them more earthquake-resistant. In addition, it is important to make sure that heavy objects are securely fastened to the ground or walls, and to secure heavy furniture, appliances, and other objects that could fall and cause injury or damage during an earthquake.
In conclusion, earthquakes are powerful and potentially destructive events that can have a significant impact on communities. By understanding the science behind earthquakes, taking steps to prepare for them, and following proper safety protocols, we can reduce the risk of damage and protect ourselves and our communities in the event of an earthquake.